|
What Does RO Remove?
Except for distillation, RO is the only known process which can dramatically reduce the following types of impurities: 1. Particulate matter, turbidity, sediment 2. Colloidal Matter 3. Total Dissolved Solids 4. Toxic Metals 5. Radioactive elements 6. Microorganisms 7. Fluoride/fluorine 8. Asbestos 9. Pesticides and Herbicides 10. Heavier organic molecules (MW>300) |
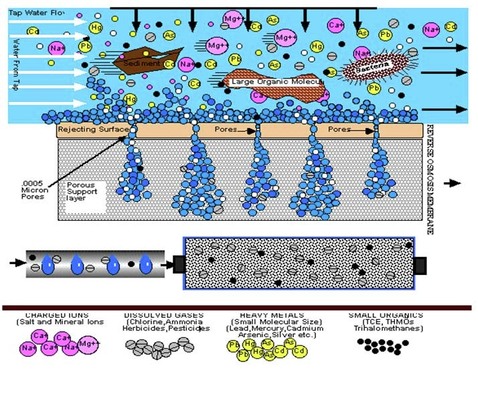
REVERSE OSMOSIS, HOW DOES IT WORK?
Reverse Osmosis membrane is able to remove and reject a wide spectrum of impurities from water and do it with very minimal energy usage. In fact, it just requires water pressure. RO produces the purest and freshest water available because it cleans water molecule by molecule. Reverse Osmosis actually purifies your drinking water, whereas filters strain or filter water. TWO DISTINCT FUNCTIONS OF RO: First, RO is the ultimate mechanical filter, or ultrafilter, straining out virtually all particulate matter, turbidity, bacteria, microorganisms, asbestos-even single molecules of the heavier organics. To appreciate the fineness of this ultrafilter, its pores are on the order of .0005 microns or .0000002 (two ten-millionths) of an inch! That's smaller than can be seen by the best optical microscopes. Second, The flow of water passing over the Reverse Osmosis membrane creates a molecular charge that causes contaminants to be repelled away from the membrane surface, while pure water molecules and oxygen are actually drawn through the membrane. Even those contaminants that are smaller than the H2O molecules themselves, are diverted and washed away down the drain. As a result, dissolved solids (contaminants that are in liquid form and can not be "strained" out), minerals and metals (which have a very minuscule molecular size), can be reduced, usually by about 95-99%. Because the membrane allows only H2O and oxygen to pass through, RO oxygenates the water, which gives it a fresh vital taste. When RO is combined with carbon filtration, It reduces the entire spectrum of contaminants (minerals, metals as well as the very small organics and gas molecules that would otherwise by missed by RO). It also oxygenates the water, which gives it a fresh taste. |